Views: 14 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2023-02-01 Origin: Site
The CWDM, DWDM, MWDM, and LWDM that are often seen now, what do these WDMs mean and what are the differences?
WDM, the full name is Wavelength Division Multiplexing, wavelength division multiplexing. It is a technology that combines multiple optical signals of different wavelengths through a multiplexer and couples them into the same optical fiber for data transmission.
How WDM works
Wavelength × frequency = speed of light (constant value), so wavelength division multiplexing is actually frequency division multiplexing
In simple terms, we can also regard WDM as a highway - different types of vehicles pour into this highway, and then part ways after arriving at the destination.
The role of WDM is to increase the transmission capacity of optical fibers and improve the utilization efficiency of optical fiber resources.
For a WDM system, in order to make it work properly, it is obvious to control the wavelength (frequency) of each optical signal. If the wavelength interval is too short, it is easy to "crash". If the wavelength interval is too long, the utilization rate is very low.
In the early days, the technical conditions were limited, and the wavelength interval would be controlled at tens of nm. This relatively dispersed wavelength division multiplexing is called sparse wavelength division multiplexing, that is, CWDM (Coarse WDM).
Later, the technology became more and more advanced, and the wavelength interval became shorter and shorter. At the level of a few nm, it became a compact WDM, called Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing, or DWDM (Dense WDM).
The wavelength interval of CWDM is 20nm, the wavelength range is from 1270nm to 1610nm, and there are 18 wave bands.
However, because the 1270-1470nm band has obvious attenuation increase, many old-type optical fibers cannot be used normally, so CWDM generally prefers to use the 8 bands of 1470-1610nm.
The wavelength interval of DWDM can be 1.6nm, 0.8nm, 0.4nm, 0.2nm, and can accommodate 40, 80, 160 waves (up to 192 waves). The wavelength range of DWDM is 1525nm to 1565nm (C band) and 1570nm to 1610nm (L band).
DWDM commonly used C-band, wavelength interval 0.4nm, channel frequency interval 50GHz
CWDM and DWDM are more common. Next, let me talk about MWDM and LWDM.
MWDM is medium wavelength division multiplexing. This is China Mobile's favorite, along with its semi-active fronthaul solution (also known as Open WDM).
The principle of MWDM is to reuse the first 6 waves of 25G CWDM. By increasing the temperature control of TEC (Thermal Electronic Cooler, semiconductor cooler), the wavelength is shifted left and right by 3.5nm to form 12 wavelengths.
6 WAVES TO 12 WAVES
This solution not only reuses the CWDM industry chain, but also meets China Mobile's own 10km forward transmission distance requirements, and also saves a lot of optical fiber resources, which can be said to serve multiple purposes.
Let's take a look at LWDM again.
LWDM is Ethernet channel-based wavelength division multiplexing (LAN WDM), and some people call it fine wavelength division multiplexing.
It expands from the existing 8 waves to 12 waves according to the channel spacing of 800GHz. The wavelength is shown in the figure below:
12 waves of LWDM
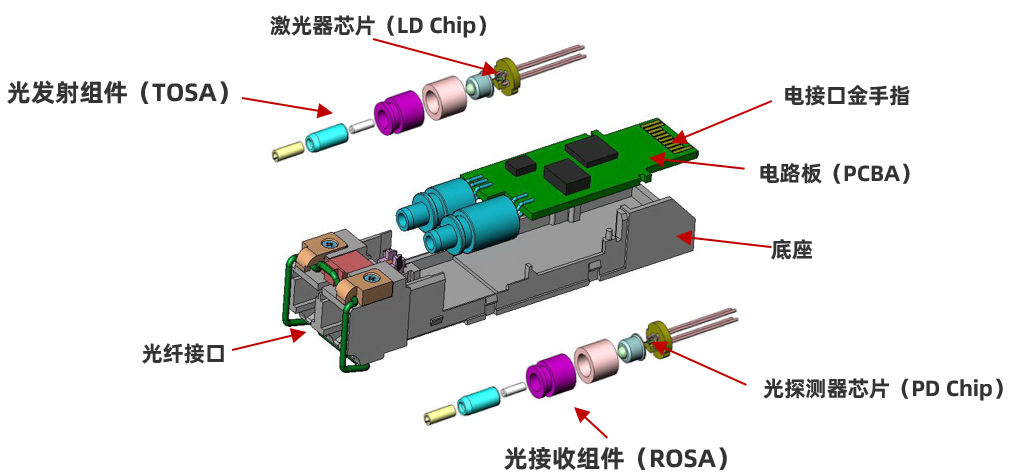
DML refers to the direct modulator laser (Directly Modulated Laser) at the TOSA transmitting end of the optical module, and corresponds to EML (Electlro-absorption Modulated Laser, electro-absorption modulated laser). EML costs more. PIN refers to the diode at the receiving end of the optical module ROSA.
The above is the basic knowledge about WDM and its branches. The reason why we focus on it is because FINEWIN acts as an agent for optical isolator used in the field of optical communications and related components in optical modules, and can process ceramics and magnetic materials for WDM. Welcome your inquiry!
Wavelength × frequency = speed of light (constant value), so wavelength division multiplexing is actually frequency division multiplexing